 |
H2Lib
3.0
|
 |
H2Lib
3.0
|
This module contains main algorithms to solve boundary element method problems in 2 dimensional space. More...
Data Structures | |
| struct | _bem2d |
| Main container object for computation of BEM related matrices and vectors. More... | |
| struct | _kernelbem2d |
| Substructure containing callback functions to different types of kernel evaluations. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct _bem2d | bem2d |
| typedef bem2d * | pbem2d |
| typedef const bem2d * | pcbem2d |
| typedef struct _aprxbem2d | aprxbem2d |
| typedef aprxbem2d * | paprxbem2d |
| typedef const aprxbem2d * | pcaprxbem2d |
| typedef struct _parbem2d | parbem2d |
| typedef parbem2d * | pparbem2d |
| typedef const parbem2d * | pcparbem2d |
| typedef struct _kernelbem2d | kernelbem2d |
| typedef kernelbem2d * | pkernelbem2d |
| typedef const kernelbem2d * | pckernelbem2d |
| typedef void(* | quadpoints2d) (pcbem2d bem, const real bmin[2], const real bmax[2], const real delta, real(**Z)[2], real(**N)[2]) |
| Callback function type for parameterizations. More... | |
| typedef enum _basisfunctionbem2d | basisfunctionbem2d |
| typedef field(* | boundary_func2d) (const real *x, const real *n) |
Enumerations | |
| enum | _basisfunctionbem2d { BASIS_NONE_BEM2D = 0, BASIS_CONSTANT_BEM2D = 'c', BASIS_LINEAR_BEM2D = 'l' } |
| Possible types of basis functions. More... | |
Functions | |
| pbem2d | new_bem2d (pccurve2d gr) |
| Main constructor for bem2d objects. More... | |
| void | del_bem2d (pbem2d bem) |
| Destructor for bem2d objects. More... | |
| pclustergeometry | build_bem2d_const_clustergeometry (pcbem2d bem, uint **idx) |
| Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using piecewise constant basis functions. More... | |
| pclustergeometry | build_bem2d_linear_clustergeometry (pcbem2d bem, uint **idx) |
| Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using linear basis functions. More... | |
| pclustergeometry | build_bem2d_clustergeometry (pcbem2d bem, uint **idx, basisfunctionbem2d basis) |
| Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using the type of basis functions specified by basis. More... | |
| pcluster | build_bem2d_cluster (pcbem2d bem, uint clf, basisfunctionbem2d basis) |
| Creates a clustertree for specified basis functions. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_recomp_bem2d (pbem2d bem, bool recomp, real accur_recomp, bool coarsen, real accur_coarsen) |
| Initialize the bem object for on the fly recompression techniques. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_row_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m) |
| This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within the row cluster. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_col_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m) |
| This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within the column cluster. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_mixed_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m) |
| This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within one of row or column cluster. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row cluster . More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_col_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with column cluster . More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_mixed_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with one of row or column cluster . More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_row_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, real accur, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_col_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, real accur, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with column cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_mixed_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, real accur, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row or column cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_aca_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, real accur) |
| Approximate matrix block with ACA using full pivoting. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_paca_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, real accur) |
| Approximate matrix block with ACA using partial pivoting. More... | |
| void | setup_hmatrix_aprx_hca_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pccluster rc, pccluster cc, pcblock tree, uint m, real accur) |
| Approximate matrix block with hybrid cross approximation using Interpolation and ACA with full pivoting. More... | |
| void | setup_h2matrix_recomp_bem2d (pbem2d bem, bool hiercomp, real accur_hiercomp) |
| Enables hierarchical recompression for hmatrices. More... | |
| void | setup_h2matrix_aprx_inter_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pcclusterbasis rb, pcclusterbasis cb, pcblock tree, uint m) |
| Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with tensorinterpolation. More... | |
| void | setup_h2matrix_aprx_greenhybrid_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pcclusterbasis rb, pcclusterbasis cb, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, real accur, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with green's method and ACA based recompression. More... | |
| void | setup_h2matrix_aprx_greenhybrid_ortho_bem2d (pbem2d bem, pcclusterbasis rb, pcclusterbasis cb, pcblock tree, uint m, uint l, real delta, real accur, quadpoints2d quadpoints) |
| Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with green's method and ACA based recompression. The resulting clusterbasis will be orthogonal. More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_hmatrix (pbem2d bem, pblock b, phmatrix G) |
| Fills an hmatrix with a predefined approximation technique. More... | |
| void | assemblecoarsen_bem2d_hmatrix (pbem2d bem, pblock b, phmatrix G) |
| Fills an hmatrix with a predefined approximation technique using coarsening strategy. More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_h2matrix_row_clusterbasis (pcbem2d bem, pclusterbasis rb) |
This function computes the matrix entries for the nested clusterbasis 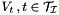 . More... . More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_h2matrix_col_clusterbasis (pcbem2d bem, pclusterbasis cb) |
This function computes the matrix entries for the nested clusterbasis 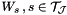 . More... . More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_h2matrix (pbem2d bem, pblock b, ph2matrix G) |
| Fills an h2matrix with a predefined approximation technique. More... | |
| void | assemblehiercomp_bem2d_h2matrix (pbem2d bem, pblock b, ph2matrix G) |
| Fills an h2matrix with a predefined approximation technique using hierarchical recompression. More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_lagrange_const_amatrix (const uint *idx, pcavector px, pcavector py, pcbem2d bem, pamatrix V) |
This function will integrate Lagrange polynomials on the boundary domain using piecewise constant basis function and store the results in a matrix V. More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_dn_lagrange_const_amatrix (const uint *idx, pcavector px, pcavector py, pcbem2d bem, pamatrix V) |
This function will integrate the normal derivatives of the Lagrange polynomials on the boundary domain using piecewise constant basis function and store the results in a matrix V. More... | |
| void | assemble_bem2d_lagrange_amatrix (const real(*X)[2], pcavector px, pcavector py, pamatrix V) |
This function will evaluate the Lagrange polynomials in a given point set X and store the results in a matrix V. More... | |
| void | projectl2_bem2d_const_avector (pbem2d bem, field(*rhs)(const real *x, const real *n), pavector f) |
Computes the 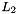 -projection of a given function using piecewise constant basis functions. More... -projection of a given function using piecewise constant basis functions. More... | |
| void | build_bem2d_rect_quadpoints (pcbem2d bem, const real a[2], const real b[2], const real delta, real(**Z)[2], real(**N)[2]) |
| Generating quadrature points, weights and normal vectors on a rectangular parameterization. More... | |
| void | build_bem2d_circle_quadpoints (pcbem2d bem, const real a[2], const real b[2], const real delta, real(**Z)[2], real(**N)[2]) |
| Generating quadrature points, weights and normal vectors on a circular parameterization. More... | |
| prkmatrix | build_bem2d_rkmatrix (pccluster row, pccluster col, void *data) |
For a block defined by row and col this function will build a rank-k-approximation and return the rkmatrix. More... | |
| pamatrix | build_bem2d_amatrix (pccluster row, pccluster col, void *data) |
For a block defined by row and col this function will compute the full submatrix and return an amatrix. More... | |
This module contains main algorithms to solve boundary element method problems in 2 dimensional space.
bem2d provides basic functionality for a general BEM-application. Considering a special problem such as the Laplace-equation one has to include the laplacebem2d module, which provides the essential quadrature routines of the kernel functions. The bem2d module consists of a struct called bem2d, which contains a collection of callback functions, that regulates the whole computation of fully-populated BEM-matrices and also of h- and h2-matrices.
| typedef struct _aprxbem2d aprxbem2d |
aprxbem2d is just an abbreviation for the struct _aprxbem2d hidden inside the bem2d.c file. This struct is necessary because of the different approximation techniques offered by this library. It will hide all dispensable information from the user.
| typedef enum _basisfunctionbem2d basisfunctionbem2d |
This is just an abbreviation for the enum _basisfunctionbem2d .
Defining a type for function that map from the boundary  of the domain to a field
of the domain to a field  .
.
This type is used to define functions that produce example dirichlet and neumann data.
| x | 2D-point the boundary  . . |
| n | Corresponding outpointing normal vector to x. |
x with normal vector n. | typedef struct _kernelbem2d kernelbem2d |
kernelbem2d is just an abbreviation for the struct _kernelbem2d. It contains a collection of callback functions to evaluate or integrate kernel function and its derivatives.
| typedef aprxbem2d* paprxbem2d |
Pointer to a aprxbem2d object.
| typedef struct _parbem2d parbem2d |
parbem2d is just an abbreviation for the struct _parbem2d , which is hidden inside the bem2d.c . It is necessary for parallel computation on h- and and h2matrices.
| typedef const aprxbem2d* pcaprxbem2d |
Pointer to a constant aprxbem2d object.
| typedef const kernelbem2d* pckernelbem2d |
Pointer to a constant kernelbem2d object.
| typedef const parbem2d* pcparbem2d |
Pointer to a constant parbem2d object.
| typedef kernelbem2d* pkernelbem2d |
Pointer to a kernelbem2d object.
| typedef void(* quadpoints2d) (pcbem2d bem, const real bmin[2], const real bmax[2], const real delta, real(**Z)[2], real(**N)[2]) |
Callback function type for parameterizations.
quadpoints2d defines a class of callback functions that are used to compute quadrature points, weight and normal vectors corresponding to the points on a given parameterization, which are used within the green's approximation functions. The parameters are in ascending order:
| bem | Reference to the bem2d object. |
| bmin | A 2D-array determining the minimal spatial dimensions of the bounding box the parameterization is located around. |
| bmax | A 2D-array determining the maximal spatial dimensions of the bounding box the parameterization is located around. |
| delta | Defines the distant between bounding box and the parameterization. |
| Z | The quadrature points will be stored inside of Z . |
| N | The outer normal vectors will be stored inside of N . For a quadrature point  , a corresponding quadrature weight , a corresponding quadrature weight  and the proper normal vector and the proper normal vector  the vector will not have unit length but the vector will not have unit length but  . . |
| enum _basisfunctionbem2d |
Possible types of basis functions.
This enum defines all possible values usable for basis functions for either neumann- and dirichlet-data. The values should be self-explanatory.
| void assemble_bem2d_dn_lagrange_const_amatrix | ( | const uint * | idx, |
| pcavector | px, | ||
| pcavector | py, | ||
| pcbem2d | bem, | ||
| pamatrix | V | ||
| ) |
This function will integrate the normal derivatives of the Lagrange polynomials on the boundary domain using piecewise constant basis function and store the results in a matrix V.
The matrix entries of V will be computed as
![\[ \left( V \right)_{i\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \frac{\partial \mathcal L_\mu}{\partial n} (\vec x) \, \mathrm d \vec x \]](../../form_235.png)
with Lagrange polynomial  defined as:
defined as:
![\[ \mathcal L_\mu (\vec x) := \left( \prod_{\nu_1 = 1, \nu_1 \neq \mu_1}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_1} - x_1}{\xi_{\nu_1} - \xi_{\mu_1}} \right) \cdot \left( \prod_{\nu_2 = 1, \nu_2 \neq \mu_2}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_2} - x_2}{\xi_{\nu_2} - \xi_{\mu_2}} \right) \]](../../form_233.png)
| idx | This array describes the permutation of the degrees of freedom. Its length is determined by V->rows . In case idx == NULL it is assumed the degrees of freedom are  instead. instead. |
| px | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in x-direction. |
| py | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in y-direction. |
| bem | BEM-object containing additional information for computation of the matrix entries. |
| V | Matrix to store the computed results as stated above. |
Fills an h2matrix with a predefined approximation technique.
This will traverse the block tree until it reaches its leafs. For a leaf block either the full matrix  is computed or a uniform rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as
is computed or a uniform rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as 
 and
and  have to be computed before calling this function because some approximation schemes depend on information residing within the clusterbasis.
have to be computed before calling this function because some approximation schemes depend on information residing within the clusterbasis.| void assemble_bem2d_h2matrix_col_clusterbasis | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| pclusterbasis | cb | ||
| ) |
This function computes the matrix entries for the nested clusterbasis 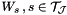 .
.
This algorithm completely traverses the clustertree belonging to the given clusterbasis until it reaches its leafs. In each leaf cluster the matrix  will be constructed and stored within the clusterbasis. In non leaf clusters the transfer matrices
will be constructed and stored within the clusterbasis. In non leaf clusters the transfer matrices  will be computed and it holds
will be computed and it holds
![\[ W_s = \begin{pmatrix} W_{s_1} & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & W_{s_\sigma} \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} F_{s_1} \\ \vdots \\ F_{s_\sigma} \end{pmatrix} \]](../../form_228.png)
A matrices  will be stored within the clusterbasis belonging to the
will be stored within the clusterbasis belonging to the 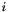 -th son.
-th son.
| bem | bem2d object containing all necessary information for computing the entries of clusterbasis rb . |
| cb | Row clusterbasis to be filled. |
| void assemble_bem2d_h2matrix_row_clusterbasis | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| pclusterbasis | rb | ||
| ) |
This function computes the matrix entries for the nested clusterbasis 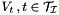 .
.
This algorithm completely traverses the clustertree belonging to the given clusterbasis until it reaches its leafs. In each leaf cluster the matrix  will be constructed and stored within the clusterbasis. In non leaf clusters the transfer matrices
will be constructed and stored within the clusterbasis. In non leaf clusters the transfer matrices  will be computed and it holds
will be computed and it holds
![\[ V_t = \begin{pmatrix} V_{t_1} & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & V_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} \]](../../form_223.png)
A matrices  will be stored within the clusterbasis belonging to the
will be stored within the clusterbasis belonging to the 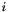 -th son.
-th son.
| bem | bem2d object containing all necessary information for computing the entries of clusterbasis rb . |
| rb | Row clusterbasis to be filled. |
Fills an hmatrix with a predefined approximation technique.
This will traverse the block tree until it reaches its leafs. For a leaf block either the full matrix  is computed or a rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as
is computed or a rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as 
This function will evaluate the Lagrange polynomials in a given point set X and store the results in a matrix V.
The matrix entries of V will be computed as
![\[ \left( V \right)_{i\mu} := \mathcal L_\mu (\vec x_i) \]](../../form_236.png)
with Lagrange polynomial  defined as:
defined as:
![\[ \mathcal L_\mu (\vec x) := \left( \prod_{\nu_1 = 1, \nu_1 \neq \mu_1}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_1} - x_1}{\xi_{\nu_1} - \xi_{\mu_1}} \right) \cdot \left( \prod_{\nu_2 = 1, \nu_2 \neq \mu_2}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_2} - x_2}{\xi_{\nu_2} - \xi_{\mu_2}} \right) \]](../../form_233.png)
| X | An array of 2D-vectors. X[i][0] will be the first component of the i-th vector. Analogously X[i][1] will be the second component of the i-th vector. The length of this array is determined by V->cols . |
| px | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in x-direction. |
| py | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in y-direction. |
| V | Matrix to store the computed results as stated above. |
| void assemble_bem2d_lagrange_const_amatrix | ( | const uint * | idx, |
| pcavector | px, | ||
| pcavector | py, | ||
| pcbem2d | bem, | ||
| pamatrix | V | ||
| ) |
This function will integrate Lagrange polynomials on the boundary domain using piecewise constant basis function and store the results in a matrix V.
The matrix entries of V will be computed as
![\[ \left( V \right)_{i\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \mathcal L_\mu (\vec x) \, \mathrm d \vec x \]](../../form_231.png)
with Lagrange polynomial  defined as:
defined as:
![\[ \mathcal L_\mu (\vec x) := \left( \prod_{\nu_1 = 1, \nu_1 \neq \mu_1}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_1} - x_1}{\xi_{\nu_1} - \xi_{\mu_1}} \right) \cdot \left( \prod_{\nu_2 = 1, \nu_2 \neq \mu_2}^m \frac{\xi_{\nu_2} - x_2}{\xi_{\nu_2} - \xi_{\mu_2}} \right) \]](../../form_233.png)
| idx | This array describes the permutation of the degrees of freedom. Its length is determined by V->rows . In case idx == NULL it is assumed the degrees of freedom are  instead. instead. |
| px | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in x-direction. |
| py | A Vector of type avector that contains interpolation points in y-direction. |
| bem | BEM-object containing additional information for computation of the matrix entries. |
| V | Matrix to store the computed results as stated above. |
Fills an hmatrix with a predefined approximation technique using coarsening strategy.
This will traverse the block tree until it reaches its leafs. For a leaf block either the full matrix  is computed or a rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as
is computed or a rank-k-approximation specified within the bem2d object is created as  While traversing the block tree backwards coarsening algorithm determines whether current non leaf block could be stored more efficiently as a single compressed leaf block in rank-k-format or not.
While traversing the block tree backwards coarsening algorithm determines whether current non leaf block could be stored more efficiently as a single compressed leaf block in rank-k-format or not.
Fills an h2matrix with a predefined approximation technique using hierarchical recompression.
This functions does not need to initialized by an appropriate approximation technique for h2matrices. Instead one needs to specify a valid approximation scheme for hmatrices such as setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_row_bem2d. When this method is finished not only the h2matrix G is filled but also the corresponding row and column clusterbasis.
 and
and  has to be allocated before calling this function.
has to be allocated before calling this function. For a block defined by row and col this function will compute the full submatrix and return an amatrix.
This function will simply create a new amatrix and call ((pcbem2d)data)->nearfield to compute the submatrix for this block.
| row | Row cluster defining the current hmatrix block. |
| col | Column cluster defining the current hmatrix block. |
| data | This object has to be a valid bem2d object. |
 .
. | void build_bem2d_circle_quadpoints | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| const real | a[2], | ||
| const real | b[2], | ||
| const real | delta, | ||
| real(**) | Z[2], | ||
| real(**) | N[2] | ||
| ) |
Generating quadrature points, weights and normal vectors on a circular parameterization.
This function will build quadrature points, weight and appropriate outpointing normal vectors on a circular parameterization. The quadrature points are stored in parameter Z, for which storage will be allocated, the normal vectors and weights are stored within N and also storage will be allocated from this function.
| bem | BEM-object containing additional information for computation of the quadrature points, weight and normal vectors. |
| a | Minimal extent of the bounding box the parameterization will be constructed around. |
| b | Maximal extent of the bounding box the parameterization will be constructed around. |
| delta | Relative distance in terms of  the parameterization is afar from the bounding box the parameterization is afar from the bounding box 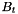 . . |
| Z | Resulting quadrature Points on the parameterization as array of 2D-vectors. Z[i][0] will be the first component of the i-th vector. Analogously Z[i][1] will be the second component of the i-th vector. The length of this array is defined within the function itself and the user has to know the length on his own. |
| N | Resulting quadrature weight and normal vectors on the parameterization as array of 2D-vectors. N[i][0] will be the first component of the i-th vector. Analogously N[i][1] will be the second component of the i-th vector. The length of this array is defined within the function itself and the user has to know the length on his own. Vectors do not have unit length instead it holds:
|
| pcluster build_bem2d_cluster | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| uint | clf, | ||
| basisfunctionbem2d | basis | ||
| ) |
Creates a clustertree for specified basis functions.
This function will build up a clustertree for a BEM-problem using basis functions of type basis. The maximal size of the leaves of the resulting tree are limited by clf. At first this function will call build_bem2d_clustergeometry and uses the temporary result to contruct a clustertree using build_adaptive_cluster.
| bem | At this stage bem just serves as a container for the geometry bem->gr itself. |
| clf | This parameter limits the maximals size of leafclusters. It holds:
|
| basis | This defines the type of basis functions that should be used to construct the cluster object. According to the type basisfunctionbem2d there are actual just to valid valued for basis: Either BASIS_CONSTANT_BEM2D or BASIS_LINEAR_BEM2D. |
| pclustergeometry build_bem2d_clustergeometry | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| uint ** | idx, | ||
| basisfunctionbem2d | basis | ||
| ) |
Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using the type of basis functions specified by basis.
The geometry is taken from the bem object as bem->gr .
| bem | At this stage bem just serves as a container for the geometry bem->gr itself. |
| idx | This method will allocate enough memory into idx to enumerate each degree of freedom. After calling build_bem2d_clustergeometry the value of idx will be 0, 1, ... N-1 if N is the number of degrees of freedom for basis functions defined by basis. |
| basis | This defines the type of basis functions that should be used to construct the clustergeometry object. According to the type basisfunctionbem2d there are actual just to valid valued for basis: Either BASIS_CONSTANT_BEM2D or BASIS_LINEAR_BEM2D. Depending on that value either build_bem2d_const_clustergeometry or build_bem2d_linear_clustergeometry will be called to build the object. |
| pclustergeometry build_bem2d_const_clustergeometry | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| uint ** | idx | ||
| ) |
Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using piecewise constant basis functions.
The geometry is taken from the bem object as bem->gr .
| bem | At this stage bem just serves as a container for the geometry bem->gr itself. |
| idx | This method will allocate enough memory into idx to enumerate each degree of freedom. After calling build_bem2d_const_clustergeometry the value of idx will be 0, 1, ... N-1 if N is the number of degrees of freedom for piecewise constant basis functions, which will be equal to the number of edges in the geometry. |
| pclustergeometry build_bem2d_linear_clustergeometry | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| uint ** | idx | ||
| ) |
Creates a clustergeometry object for a BEM-Problem using linear basis functions.
The geometry is taken from the bem object as bem->gr .
| bem | At this stage bem just serves as a container for the geometry bem->gr itself. |
| idx | This method will allocate enough memory into idx to enumerate each degree of freedom. After calling build_bem2d_linear_clustergeometry the value of idx will be 0, 1, ... N-1 if N is the number of degrees of freedom for linear basis functions, which will be equal to the number of vertices in the geometry. |
| void build_bem2d_rect_quadpoints | ( | pcbem2d | bem, |
| const real | a[2], | ||
| const real | b[2], | ||
| const real | delta, | ||
| real(**) | Z[2], | ||
| real(**) | N[2] | ||
| ) |
Generating quadrature points, weights and normal vectors on a rectangular parameterization.
This function will build quadrature points, weight and appropriate outpointing normal vectors on a rectangular parameterization. The quadrature points are stored in parameter Z, for which storage will be allocated, the normal vectors and weights are stored within N and also storage will be allocated from this function.
| bem | BEM-object containing additional information for computation of the quadrature points, weight and normal vectors. |
| a | Minimal extent of the bounding box the parameterization will be constructed around. |
| b | Maximal extent of the bounding box the parameterization will be constructed around. |
| delta | Relative distance in terms of  the parameterization is afar from the bounding box the parameterization is afar from the bounding box 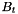 . . |
| Z | Resulting quadrature Points on the parameterization as array of 2D-vectors. Z[i][0] will be the first component of the i-th vector. Analogously Z[i][1] will be the second component of the i-th vector. The length of this array is defined within the function itself and the user has to know the length on his own. |
| N | Resulting quadrature weight and normal vectors on the parameterization as array of 2D-vectors. N[i][0] will be the first component of the i-th vector. Analogously N[i][1] will be the second component of the i-th vector. The length of this array is defined within the function itself and the user has to know the length on his own. Vectors do not have unit length instead it holds:
|
For a block defined by row and col this function will build a rank-k-approximation and return the rkmatrix.
This function will simply create a new rkmatrix and call ((pcbem2d)data)->farfield_rk to create the rank-k-approximation of this block.
| row | Row cluster defining the current hmatrix block. |
| col | Column cluster defining the current hmatrix block. |
| data | This object has to be a valid and initialized bem2d object. |
| void del_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem | ) |
Main constructor for bem2d objects.
Primary constructor for bem2d objects. Although a valid bem2d object will be returned it is not intended to use this constructor. Instead use a problem specific constructor such as new_slp_laplace_bem2d or new_dlp_laplace_bem2d .
| gr | 2D geometry described as polygonal mesh. |
| void projectl2_bem2d_const_avector | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| field(*)(const real *x, const real *n) | rhs, | ||
| pavector | f | ||
| ) |
Computes the 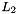 -projection of a given function using piecewise constant basis functions.
-projection of a given function using piecewise constant basis functions.
In case of piecewise constant basis functions the 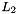 -projection of a function
-projection of a function 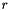 is defined as:
is defined as:
![\[ f_i := \frac{1}{\lvert \Gamma_i \rvert} \, \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, r(\vec x, n(\vec x) ) \, \mathrm d \vec x \, , \]](../../form_239.png)
with  meaning the area of triangle
meaning the area of triangle 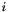 and
and  being the outpointing normal vector at the point
being the outpointing normal vector at the point  .
.
| bem | BEM-object containing additional information for computation of the vector entries. |
| rhs | This callback defines the function to be  projected. Its arguments are an evaluation 2D-vector projected. Its arguments are an evaluation 2D-vector x and its normal vector n. |
| f | The  -projection coefficients are stored within this vector. Therefore its length has to be at least -projection coefficients are stored within this vector. Therefore its length has to be at least bem->gr->edges. |
| void setup_h2matrix_aprx_greenhybrid_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pcclusterbasis | rb, | ||
| pcclusterbasis | cb, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| real | accur, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with green's method and ACA based recompression.
In case of lead clusters, we use the techniques from setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_row_bem2d and setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_col_bem2d and construct two algebraic interpolation operators  and
and  and approximate an admissible block
and approximate an admissible block  by
by
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx I_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, I_s^* \, . \]](../../form_209.png)
This yields the representation:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx I_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, I_s^* = V_t \, R_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, R_s^* \, W_s^* = V_t \, S_b \, W_s^* \]](../../form_210.png)
with  just a
just a  -matrix taking just the pivot rows and columns of the original matrix
-matrix taking just the pivot rows and columns of the original matrix  .
.
In case of non leaf clusters transfer matrices  and
and  are also introduced and the approximation of the block looks like:
are also introduced and the approximation of the block looks like:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx \begin{pmatrix} V_{t_1} & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & V_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} S_b \, \begin{pmatrix} F_{s_1}^* & \cdots & F_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} W_{s_1}^* & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & W_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \]](../../form_206.png)
The transfer matrices are build up in the following way: At first for a non leaf cluster  we construct a matrix
we construct a matrix  as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d but not with the index set
as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d but not with the index set  but with the index set
but with the index set
![\[ \bigcup_{t' \in \operatorname{sons}(t)} \, R_{t'} \, . \]](../../form_215.png)
Then again we use adaptive cross approximation technique to receive
![\[ A_t \approx C_t \, D_t^* \, . \]](../../form_216.png)
And again we construct an interpolation operator as before:
![\[ I_t := C_t \left( R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \, R_t \]](../../form_217.png)
And finally we have to solve
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} = C_t \left( R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \]](../../form_218.png)
for our desired  .
.
Respectively the transfer matrices for the column clusterbasis are constructed.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rb | Root of the row clusterbasis. |
| cb | Root of the column clusterbasis. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 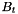 or or 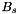 and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_h2matrix_aprx_greenhybrid_ortho_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pcclusterbasis | rb, | ||
| pcclusterbasis | cb, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| real | accur, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with green's method and ACA based recompression. The resulting clusterbasis will be orthogonal.
In case of leaf clusters, we use the techniques similar to setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_row_bem2d and setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_col_bem2d and construct two algebraic interpolation operators  and
and  and approximate an admissible block
and approximate an admissible block  by
by
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx I_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, I_s^* \, . \]](../../form_209.png)
This yields the representation:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx I_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, I_s^* = V_t \, R_t \, G_{| t \times s} \, R_s^* \, W_s^* = V_t \, S_b \, W_s^* \]](../../form_210.png)
with  just a
just a  -matrix taking just the pivot rows and columns of the original matrix
-matrix taking just the pivot rows and columns of the original matrix  .
.
In case of non leaf clusters transfer matrices  and
and  are also introduced and the approximation of the block looks like:
are also introduced and the approximation of the block looks like:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx \begin{pmatrix} V_{t_1} & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & V_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} S_b \, \begin{pmatrix} F_{s_1}^* & \cdots & F_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} W_{s_1}^* & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & W_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \]](../../form_206.png)
The transfer matrices are build up in the following way: At first for a non leaf cluster  we construct a matrix
we construct a matrix  as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d but not with the index set
as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d but not with the index set  but with the index set
but with the index set
![\[ \bigcup_{t' \in \operatorname{sons}(t)} \, R_{t'} \, . \]](../../form_215.png)
Then again we use adaptive cross approximation technique to receive
![\[ A_t \approx C_t \, D_t^* \, . \]](../../form_216.png)
And again we construct an interpolation operator as before:
![\[ I_t := C_t \left( R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \, R_t \]](../../form_217.png)
And finally we have to solve
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} = C_t \left( R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \]](../../form_218.png)
for our desired  .
.
Respectively the transfer matrices for the column clusterbasis are constructed.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rb | Root of the row clusterbasis. |
| cb | Root of the column clusterbasis. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 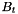 or or 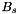 and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_h2matrix_aprx_inter_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pcclusterbasis | rb, | ||
| pcclusterbasis | cb, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m | ||
| ) |
Initialize the bem2d object for approximating a h2matrix with tensorinterpolation.
In case of leaf cluster  this approximation scheme creates a h2matrix approximation of the following form:
this approximation scheme creates a h2matrix approximation of the following form:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx V_t \, S_b \, W_s^* \]](../../form_197.png)
with the matrices defined as
![\[ \left( V_t \right)_{i\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \mathcal L_\mu(\vec x) \, \mathrm d \vec x \]](../../form_198.png)
![\[ \left( W_s \right)_{j\nu} := \int_\Gamma \, \Lambda_\nu(\vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \]](../../form_199.png)
![\[ \left( S_b \right)_{\mu\nu} := g(\vec \xi_\mu, \vec \xi_\nu) \, . \]](../../form_200.png)
Here  depends on the choice of the integral operator: in case of the single layer potential it applies
depends on the choice of the integral operator: in case of the single layer potential it applies  and in case of the double layer potential it applies
and in case of the double layer potential it applies  .
.
In case of non leaf clusters transfer matrices  and
and  are also constructed and the approximation of the block looks like:
are also constructed and the approximation of the block looks like:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx \begin{pmatrix} V_{t_1} & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & V_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} E_{t_1} \\ \vdots \\ E_{t_\tau} \end{pmatrix} S_b \, \begin{pmatrix} F_{s_1}^* & \cdots & F_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \, \begin{pmatrix} W_{s_1}^* & & \\ & \ddots & \\ & & W_{s_\sigma}^* \end{pmatrix} \]](../../form_206.png)
The transfer matrices look like
![\[ \left( E_{t_i} \right)_{\mu\mu'} := \mathcal L_{\mu}(\xi_{\mu'}) \]](../../form_207.png)
respectively
![\[ \left( F_{s_j} \right)_{\nu\nu'} := \mathcal L_{\nu}(\xi_{\nu'}) \]](../../form_208.png)
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rb | Root of the row clusterbasis. |
| cb | Root of the column clusterbasis. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of Chebyshev interpolation points in each spatial dimension. |
Enables hierarchical recompression for hmatrices.
This function enables hierarchical recompression. It is only necessary to initialize the bem2d object with some hmatrix compression technique such as setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_row_bem2d . Afterwards one just has to call assemblehiercomp_bem2d_h2matrix to create a initially compressed h2matrix approximation.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for h2-recompression are set within the bem object. |
| hiercomp | A flag to indicates whether hierarchical recompression should be used or not. |
| accur_hiercomp | The accuracy the hierarchical recompression technique will use to create a compressed h2matrix. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_aca_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| real | accur | ||
| ) |
Approximate matrix block with ACA using full pivoting.
This approximation scheme will utilize adaptive cross approximation with full pivoting to retrieve a rank-k-approximation as
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_b \, B_b^* \]](../../form_181.png)
with a given accuracy accur.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_col_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with column cluster .
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the column cluster. For an admissible block  one yields an approximation in shape of
one yields an approximation in shape of
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_{t,s} \, B_s^* \quad \text{with} \]](../../form_135.png)
![\[ \left( A_{t,s}^1 \right)_{i\nu} := \omega_\nu \, \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \frac{\partial g}{\partial n_z} (\vec x, \vec z_\nu) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad , \]](../../form_152.png)
![\[ \left( A_{t,s}^2 \right)_{i\nu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, g(\vec x, \vec z_\nu) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad , \]](../../form_153.png)
![\[ A_{t,s} = \begin{pmatrix} A^1_{t,s} & A^2_{t,s} \end{pmatrix} \quad , \]](../../form_154.png)
![\[ \left( B_s^1 \right)_{j\nu} := \int_\Gamma \, \gamma (\vec z_\nu, \vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \quad , \]](../../form_155.png)
![\[ \left( B_s^2 \right)_{j\nu} := -\omega_\nu \, \int_\Gamma \, \frac{\partial \gamma}{\partial n_z}(\vec z_\nu, \vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \quad \text{and} \]](../../form_156.png)
![\[ B_s = \begin{pmatrix} B_s^1 & B_s^2 \end{pmatrix} . \]](../../form_157.png)
 is the underlying kernel function defined by the the integral operator. In case of single layer potential it applies
is the underlying kernel function defined by the the integral operator. In case of single layer potential it applies  but in case of double layer potential it applies
but in case of double layer potential it applies  . The green quadrature points
. The green quadrature points  and the weight
and the weight  depend on the choice of
depend on the choice of quadpoints and delta, which define the parameterization around the row cluster.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 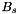 and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_mixed_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with one of row or column cluster .
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the row or column cluster depending on the diamter of their bounding boxes.. For an admissible block  one yields an approximation in shape of
one yields an approximation in shape of
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx \begin{cases} \begin{array}{ll} A_{t,s} \, B_s^* &: \operatorname{diam}(t) < \operatorname{diam}(s)\\ A_t \, B_{t,s}^* &: \operatorname{diam}(t) \geq \operatorname{diam}(s) \end{array} \end{cases} \]](../../form_159.png)
For definition of these matrices see setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d and setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_col_bem2d .
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 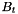 or or 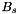 and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the Parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row cluster .
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the row cluster. For an admissible block  one yields an approximation in shape of
one yields an approximation in shape of
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_t \, B_{t,s}^* \quad \text{with} \]](../../form_129.png)
![\[ \left( A_t^1 \right)_{i\nu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, g(\vec x, \vec z_\nu) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad , \]](../../form_142.png)
![\[ \left( A_t^2 \right)_{i\nu} := \omega_\nu \, \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \frac{\partial g}{\partial n_z} (\vec x, \vec z_\nu) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad , \]](../../form_143.png)
![\[ A_t = \begin{pmatrix} A^1_t & A^2_t \end{pmatrix} \quad , \]](../../form_144.png)
![\[ \left( B_{t,s}^1 \right)_{j\nu} := \omega_\nu \, \int_\Gamma \, \frac{\partial \gamma}{\partial n_z} (\vec z_\nu, \vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \quad , \]](../../form_145.png)
![\[ \left( B_{t,s}^2 \right)_{j\nu} := -\int_\Gamma \, \gamma(\vec z_\nu, \vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \quad \text{and} \]](../../form_146.png)
![\[ B_{t,s} = \begin{pmatrix} B_{t,s}^1 & B_{t,s}^2 \end{pmatrix} . \]](../../form_147.png)
 is the underlying kernel function defined by the the integral operator. In case of single layer potential it applies
is the underlying kernel function defined by the the integral operator. In case of single layer potential it applies  but in case of double layer potential it applies
but in case of double layer potential it applies  . The green quadrature points
. The green quadrature points  and the weight
and the weight  depend on the choice of
depend on the choice of quadpoints and delta, which define the parameterization around the row cluster.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 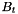 and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_col_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| real | accur, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with column cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA.
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula and ACA recompression. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the column cluster and a recompression using adaptive cross approximation.
In a first step the algorithm creates the same matrix 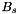 as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_col_bem2d. From this matrix we create a new approximation by using ACA with full pivoting (decomp_fullaca_rkmatrix) and we get a new rank-k-approximation of
as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_col_bem2d. From this matrix we create a new approximation by using ACA with full pivoting (decomp_fullaca_rkmatrix) and we get a new rank-k-approximation of 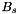 :
:
![\[ B_s \approx C_s \, D_s^* . \]](../../form_171.png)
Afterwards we define an algebraic interpolation operator
![\[ I_s := C_s \, \left(R_s \, C_s \right)^{-1} \, R_s \]](../../form_172.png)
with  selecting the pivot rows from the ACA-algorithm. Appling
selecting the pivot rows from the ACA-algorithm. Appling  to our matrix block
to our matrix block  we yield:
we yield:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx G_{| t \times s} \, I_s^* = G_{| t \times s} \, \left( C_s \, \left(R_s \, C_s \right)^{-1} \, R_s \right)^* = A_{t,s} \, W_s^* \, . \]](../../form_175.png)
This defines our final approximation of the block with the matrices
![\[ A_{t,s} := G_{| t \times s} \, R_s^* \]](../../form_176.png)
and
![\[ W_s := C_s \, \left(R_s \, C_s \right)^{-1} \, . \]](../../form_177.png)
In order to save time and storage we compute the matrices  only once for each cluster
only once for each cluster  .
.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 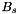 and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_mixed_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| real | accur, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row or column cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA.
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula and ACA recompression. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the row or column cluster and a recompression using adaptive cross approximation.
Depending on the rank produced by either setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_row_bem2d or setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_col_bem2d we define this approximation by
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx \begin{cases} \begin{array}{ll} V_t \, B_{t,s}* &: \operatorname{rank}(V_t) \leq \operatorname{rank}(W_s)\\ A_{t,s} \, W_s* &: \operatorname{rank}(V_t) > \operatorname{rank}(W_s) \quad . \end{array} \end{cases} \]](../../form_180.png)
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 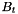 or or 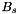 and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_greenhybrid_row_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| uint | l, | ||
| real | delta, | ||
| real | accur, | ||
| quadpoints2d | quadpoints | ||
| ) |
creating hmatrix approximation using green's method with row cluster connected with recompression technique using ACA.
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix using green's formula and ACA recompression. The approximation is based upon an expansion around the row cluster and a recompression using adaptive cross approximation.
In a first step the algorithm creates the same matrix  as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d. From this matrix we create a new approximation by using ACA with full pivoting (decomp_fullaca_rkmatrix) and we get a new rank-k-approximation of
as in setup_hmatrix_aprx_green_row_bem2d. From this matrix we create a new approximation by using ACA with full pivoting (decomp_fullaca_rkmatrix) and we get a new rank-k-approximation of  :
:
![\[ A_t \approx C_t \, D_t^* . \]](../../form_161.png)
Afterwards we define an algebraic interpolation operator
![\[ I_t := C_t \, \left(R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \, R_t \]](../../form_162.png)
with  selecting the pivot rows from the ACA-algorithm. Appling
selecting the pivot rows from the ACA-algorithm. Appling  to our matrix block
to our matrix block  we yield:
we yield:
![\[ G_{| t \times s} \approx I_t \, G_{| t \times s} = C_t \, \left(R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \, R_t \, G_{| t \times s} = V_t \, B_{t,s}^* \, . \]](../../form_166.png)
This defines our final approximation of the block with the matrices
![\[ V_t := C_t \, \left(R_t \, C_t \right)^{-1} \]](../../form_167.png)
and
![\[ B_{t,s} := \left( R_t \, G_{| t \times s} \right)^* \, . \]](../../form_168.png)
In order to save time and storage we compute the matrices  only once for each cluster
only once for each cluster  .
.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of gaussian quadrature points in each patch of the parameterization. |
| l | Number of subdivisions for gaussian quadrature in each patch of the parameterization. |
| delta | Defines the distance between the bounding box 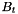 and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. and the parameterization defined by quadpoints. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| quadpoints | This callback function defines a parameterization and it has to return valid quadrature points, weight and normalvectors on the parameterization. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_hca_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m, | ||
| real | accur | ||
| ) |
Approximate matrix block with hybrid cross approximation using Interpolation and ACA with full pivoting.
At first for a block  the matrix
the matrix  with
with  is set up with
is set up with  interpolation points from
interpolation points from 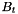 and
and  interpolation points from
interpolation points from 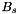 . Then applying ACA with full pivoting to
. Then applying ACA with full pivoting to  yields the representation:
yields the representation:
![\[ S_{\mu\nu} \approx \sum_{\alpha = 1}^k \sum_{\beta = 1}^k \, S_{\mu \alpha} \, \hat S_{\alpha \beta} \, S_{\beta \nu} \]](../../form_186.png)
with  and
and  defining the pivot rows and columns from the ACA algoritm. This means we can rewrite the fundamental solution
defining the pivot rows and columns from the ACA algoritm. This means we can rewrite the fundamental solution  as follows:
as follows:
![\[ g(\vec x, \vec y) \approx \sum_{\mu = 1}^{m^2 }\sum_{\nu = 1}^{m^2} \mathcal L_\mu(\vec x) \, g(\vec \xi_\mu, \vec \xi\nu) \, \mathcal L_\nu(\vec y) \approx \sum_{\mu = 1}^{m^2 }\sum_{\nu = 1}^{m^2} \sum_{\alpha = 1}^k \sum_{\beta = 1}^k \mathcal L_\mu(\vec x) \, S_{\mu \alpha} \, \hat S_{\alpha \beta} \, S_{\beta \nu} \, \mathcal L_\nu(\vec y) \]](../../form_189.png)
Now reversing the interpolation we can express this formula as:
![\[ g(\vec x, \vec y) \approx \sum_{\alpha = 1}^k \sum_{\beta = 1}^k \, \hat S_{\alpha \beta} \, \sum_{\mu = 1}^{m^2 } \, \left( \mathcal L_\mu(\vec x) \, S_{\mu \alpha} \right) \, \sum_{\nu = 1}^{m^2} \left( S_{\beta \nu} \, \mathcal L_\nu(\vec y) \right) \approx \sum_{\alpha = 1}^k \sum_{\beta = 1}^k \, g(\vec x, \vec \xi_\alpha) \, \hat S_{\alpha \beta} \, g(\vec \xi_\beta, \vec y) \]](../../form_190.png)
Depending on the condition  we can now construct the rank-k-approximation as
we can now construct the rank-k-approximation as
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx \left( A_b \, \hat S \right) \, B_b^* \quad \text{or} \]](../../form_192.png)
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_b \, \left( B_b \,\hat S \right)^* \]](../../form_193.png)
with matrices
![\[ \left( A_b \right)_{i\alpha} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi(\vec x) \, g(\vec x, \vec \xi_\alpha) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad , \]](../../form_194.png)
![\[ \left( B_b \right)_{j\beta} := \int_\Gamma \, g(\vec \xi_\beta, \vec y) \, \psi(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \quad . \]](../../form_195.png)
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of Chebyshev interpolation points in each spatial dimension. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_col_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m | ||
| ) |
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within the column cluster.
The approximation of an admissible block  is done by:
is done by:
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_{t,s} \, B_s^* \quad \text{with} \]](../../form_135.png)
![\[ \left( A_{t,s} \right)_{i\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, g(\vec x , \, \vec \xi_\mu) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad \text{and} \]](../../form_136.png)
![\[ \left( B_s \right)_{j\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \Lambda_\mu(\vec y) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \, . \]](../../form_137.png)
with  being either the Lagrange polynomial
being either the Lagrange polynomial  itself in case of single layer potential, or
itself in case of single layer potential, or  in case of double layer potential.
in case of double layer potential.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of Chebyshev interpolation points in each spatial dimension. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_mixed_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m | ||
| ) |
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within one of row or column cluster.
The interpolation depends on the condition:
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx \begin{cases}\begin{array}{ll} A_t \, B_{t,s}^* &: \operatorname{diam}(t) <\operatorname{diam}(s)\\ A_{t,s} \, B_s^* &: \operatorname{diam}(t) \geq \operatorname{diam}(s) \end{array} \end{cases} \]](../../form_141.png)
For definition of these matrices see setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_row_bem2d and setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_col_bem2d .
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of Chebyshev interpolation points in each spatial dimension. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_inter_row_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| uint | m | ||
| ) |
This function initializes the bem2d object for approximating a matrix with tensorinterpolation within the row cluster.
The approximation of an admissible block  is done by:
is done by:
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_t \, B_{t,s}^* \quad \text{with} \]](../../form_129.png)
![\[ \left( A_t \right)_{i\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \varphi_i(\vec x) \, \mathcal L_\mu(\vec x) \, \mathrm d \vec x \quad \text{and} \]](../../form_130.png)
![\[ \left( B_{t,s} \right)_{j\mu} := \int_\Gamma \, \gamma(\vec \xi_\mu , \, \vec y ) \, \psi_j(\vec y) \, \mathrm d \vec y \, . \]](../../form_131.png)
with  being the kernel function of the underlying integral operator. In case of the single layer potential this equal to the fundamental solution
being the kernel function of the underlying integral operator. In case of the single layer potential this equal to the fundamental solution  , in case of double layer potential this applies to
, in case of double layer potential this applies to  .
.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| m | Number of Chebyshev interpolation points in each spatial dimension. |
| void setup_hmatrix_aprx_paca_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| pccluster | rc, | ||
| pccluster | cc, | ||
| pcblock | tree, | ||
| real | accur | ||
| ) |
Approximate matrix block with ACA using partial pivoting.
This approximation scheme will utilize adaptive cross approximation with partial pivoting to retrieve a rank-k-approximation as
![\[ G_{|t \times s} \approx A_b \, B_b^* \]](../../form_181.png)
with a given accuracy accur.
| bem | All needed callback functions and parameters for this approximation scheme are set within the bem object. |
| rc | Root of the row clustertree. |
| cc | Root of the column clustertree. |
| tree | Root of the blocktree. |
| accur | Assesses the minimum accuracy for the ACA approximation. |
| void setup_hmatrix_recomp_bem2d | ( | pbem2d | bem, |
| bool | recomp, | ||
| real | accur_recomp, | ||
| bool | coarsen, | ||
| real | accur_coarsen | ||
| ) |
Initialize the bem object for on the fly recompression techniques.
| bem | According to the other parameters within bem->aprx there are set some flags that indicate which of the recompression techniques should be used while building up a hmatrix . |
| recomp | If this flag is set to true a blockwise recompression will be applied. For each block  independent on the approximation technique we will yield an approximation of the following kind: independent on the approximation technique we will yield an approximation of the following kind:
 depending on the accuracy accur_recomp depending on the accuracy accur_recomp |
| accur_recomp | The accuracy the blockwise recompression will used to compress a block with SVD. |
| coarsen | If a block consists of  sons which are all leafs of the blocktree, then it can be more efficient to store them as a single admissible leaf. This is done by "coarsening" recursively using the SVD. sons which are all leafs of the blocktree, then it can be more efficient to store them as a single admissible leaf. This is done by "coarsening" recursively using the SVD. |
| accur_coarsen | The accuracy the coarsen technique will use to determine the coarsened block structure. |
 1.8.11
1.8.11